 Listening Lab Malaysia offers a selection of best-rated hearing aids.
Listening Lab Malaysia offers a selection of best-rated hearing aids.

We hear sounds from different sources everyday, such as television, music on our earpods, household appliances, or the regular traffic noise. At an average rate, these noises don't damage our hearing, but when it becomes too loud, they can damage sensitive structures in the inner ear and cause what we call "Noise-induced hearing loss" (NIHL).
According to National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders,
"Sounds at or below 70 A-weighted decibels (dBA), even after long exposure, are unlikely to cause hearing loss. However, prolonged or repeated exposure to sounds at or above 85 dBA can cause hearing loss. The louder the sound, the shorter time it takes for NIHL to happen."
Sounds at or below 70 A-weighted decibels (dBA), like a normal conversation or a sound from a movie theater (74-104 dBA), are unlikely to cause hearing loss even after prolonged exposure.
However, prolonged or repeated exposure to sounds at or above 85 dBA, such as loud motorcycle noises (around 80-110 dBA), music at maximum level during sports events and concerts (90-110 dBA), sirens (110-130 dBA) or fireworks show (140-160 dBA) can cause hearing loss.
Extremely loud short noises such as gunshots or explosions can rupture the eardrum or damage the bones in the middle ear, which can cause an immediate and permanent NIHL.
Effects and Signs of NIHL
After a long period, you may start to experience hearing loss. The damage to your hearing is gradual, and you may not notice it, or you might ignore the signs of hearing loss until they become more pronounced.
You might hear distorted or muffled sounds and find it difficult to understand other people when they talk to you, and they have to raise their voice, or you have to increase the volume of the audio you are currently listening to.
If you have experienced tinnitus - a ringing, buzzing, or roaring in the ear or head, you might consider having your ear checked to avoid long-term damage.
NIHL Classification of Audiogram
“An audiogram is a graph that shows the softest sounds a person can hear at different pitches or frequencies. The closer the marks are to the top of the graph, the softer the sounds that person can hear. Where the patient's results fall on the audiogram indicate the different degrees of hearing loss. The audiogram shown below indicates the different degrees of hearing loss.” (Babyhearing.org)

Image source: BabyHearing.org
According to the National Library of Medicine's study on the classification of audiograms in preventing NIHL, "several audiogram interpretations or classification options are available – all having their associated advantages and disadvantages. Unfortunately, most of them are geared towards compensation for hearing impairment."
Occupational noise-induced hearing loss (ONIHL) contributes significantly to the burden of disabling hearing loss (Nelson, Nelson, Concha-Barrientos, & Fingernut, 2005). Over the years, data have been collected on this subject as occupational health practice begins to take root in areas where it did not exist (Stevens et al., 2011). The prevalence of ONIHL seems to depend on the method used to define it.
The value of audiometry lies in interpreting the results and actions taken after that, without which it is a compliance tick in the box with minimal benefit to the workforce.
The UK Health and Safety Executive (UKHSE) developed a simple and practical method for categorizing audiograms.
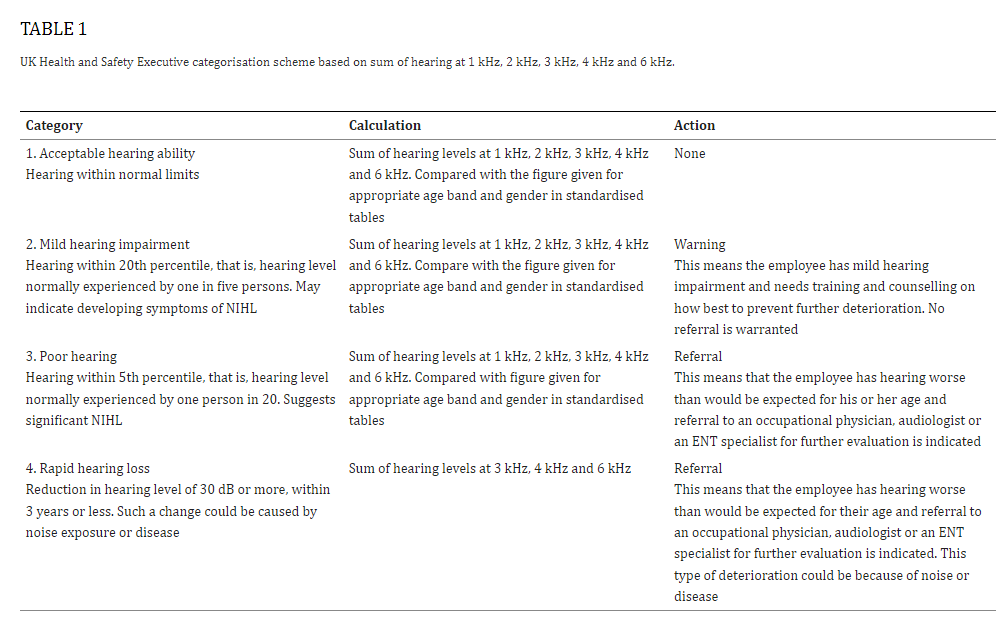
Source: Health and Safety Executive. (2005). Controlling noise at work. Guidance on regulations. The control of noise at work regulations 2005. Norwich: Health and Safety Executive.
How Does An Audiogram Measure Hearing?
During a hearing test, some sounds are presented in various ways. When sampling with earphones or loudspeakers, the sound goes into the ear canal, through the middle ear to reach the inner ear - this is known as air conduction testing. Air conduction testing looks at how the whole hearing system responds to sound.
If air conduction testing shows a hearing loss, bone conduction testing is performed. A bone vibrator is placed behind the ear to send sounds straight to the inner ear. Sounds are sent via the bones of the head. It does not pass through the eardrum or the middle ear. When something stops sounds from moving through the eardrum and middle ear, bone conduction hearing levels will be better than air conduction levels. This means a conductive hearing loss is present.
When sound usually moves through the outer and middle ear, but the inner ear does not work typically, both bone conduction and air conduction hearing levels will be the same. A sensorineural hearing loss is present.
The Bottom Line
If you (or anyone you know) is experiencing hearing loss, there could be many causes. Sometimes it may be our lifestyle. So, it is important to have them check with an audiologist to confirm hearing loss and if concerns are present, it could be addressed quickly. It might only be a temporary hearing loss, or a mild hearing loss.
You may inquire through The Listening Lab Malaysia and book an appointment with our audiologist, immediately. You may also contact us through WhatsApp @ 03 7725 9334.











